Resistor combination circuits
Several resistors can be combined to new values. So you can create resistors ,
which do not exist in the standard series. This is also useful when the colleague has again taken the last resistor
from the drawer without ordering new ones.
By cleverly combining only three resistors, any desired value can be achieved pretty accurately. You only need to know a few basic circuits and how to calculate them.
By cleverly combining only three resistors, any desired value can be achieved pretty accurately. You only need to know a few basic circuits and how to calculate them.
Combining two resistors
The simplest way to combine resistors is a series or parallel connection of two resistors.
The calculation is simplest for series connection: The total resistance consists of
Addition of the individual resistors. In the series connection the total resistance is therefore always higher
than the largest of the individual resistors.
When combining two resistors to a parallel circuit, the calculation is a bit more complicated. The total resistance is the inverse value of the addition of the inverse values of the single resistors. In the Parallel connection, the total resistance is always smaller than the smallest individual resistance.
When combining two resistors to a parallel circuit, the calculation is a bit more complicated. The total resistance is the inverse value of the addition of the inverse values of the single resistors. In the Parallel connection, the total resistance is always smaller than the smallest individual resistance.
Combining three resistors
If the desired resistor cannot be combined with the combination of two resistors
it usually helps to combine three resistors. The formulas of series and series connection
can easily be extended by an additional resistor.
By the way, the author recommends to use the parallel connection when combining resistors. It is a bit more difficult to calculate, but finally it is more clear, because it doesn't create new voltage nodes.
By the way, the author recommends to use the parallel connection when combining resistors. It is a bit more difficult to calculate, but finally it is more clear, because it doesn't create new voltage nodes.
The series and parallel connection can be extended as much as you want. For a 29 kΩ resistor
you could for example connect 29 1kΩ resistors in series. But this is neither useful
and practical. Better try it with a mixed circuit:
Mixed circuits with three combined resistors
Mixed circuits are circuits where resistors are combined in series and parallel.
With three resistors the two simplest mixed resistor circuits can be combined:
One consists of a series resistor to two parallel resistors.
The other one is a parallel resistor to two serially connected resistors.
With these combined resistors, extremely accurate total resistances can be achieved, even if the calculation is a bit complicated.
One consists of a series resistor to two parallel resistors.
The other one is a parallel resistor to two serially connected resistors.
With these combined resistors, extremely accurate total resistances can be achieved, even if the calculation is a bit complicated.
To return to the previous example from the desired 29 kΩ resistor:
If you choose the serial R1 = 27 kΩ and R2 =2.2 kΩ, you have 29.2 kΩ. So you are quite close.
If you combine in parallel to R2 another R3 of 22kΩ, the parallel connection (R2//R3) gives a value of exactly 2 kΩ.
Thus R1 + (R2//R3) = 27kΩ + 2kΩ = 29kΩ.
How to dimension these circuits and find the right resistor combinations is a matter of practice. Every electronic engineer develops his own procedure to find good combinations over time.
If you choose the serial R1 = 27 kΩ and R2 =2.2 kΩ, you have 29.2 kΩ. So you are quite close.
If you combine in parallel to R2 another R3 of 22kΩ, the parallel connection (R2//R3) gives a value of exactly 2 kΩ.
Thus R1 + (R2//R3) = 27kΩ + 2kΩ = 29kΩ.
How to dimension these circuits and find the right resistor combinations is a matter of practice. Every electronic engineer develops his own procedure to find good combinations over time.
X
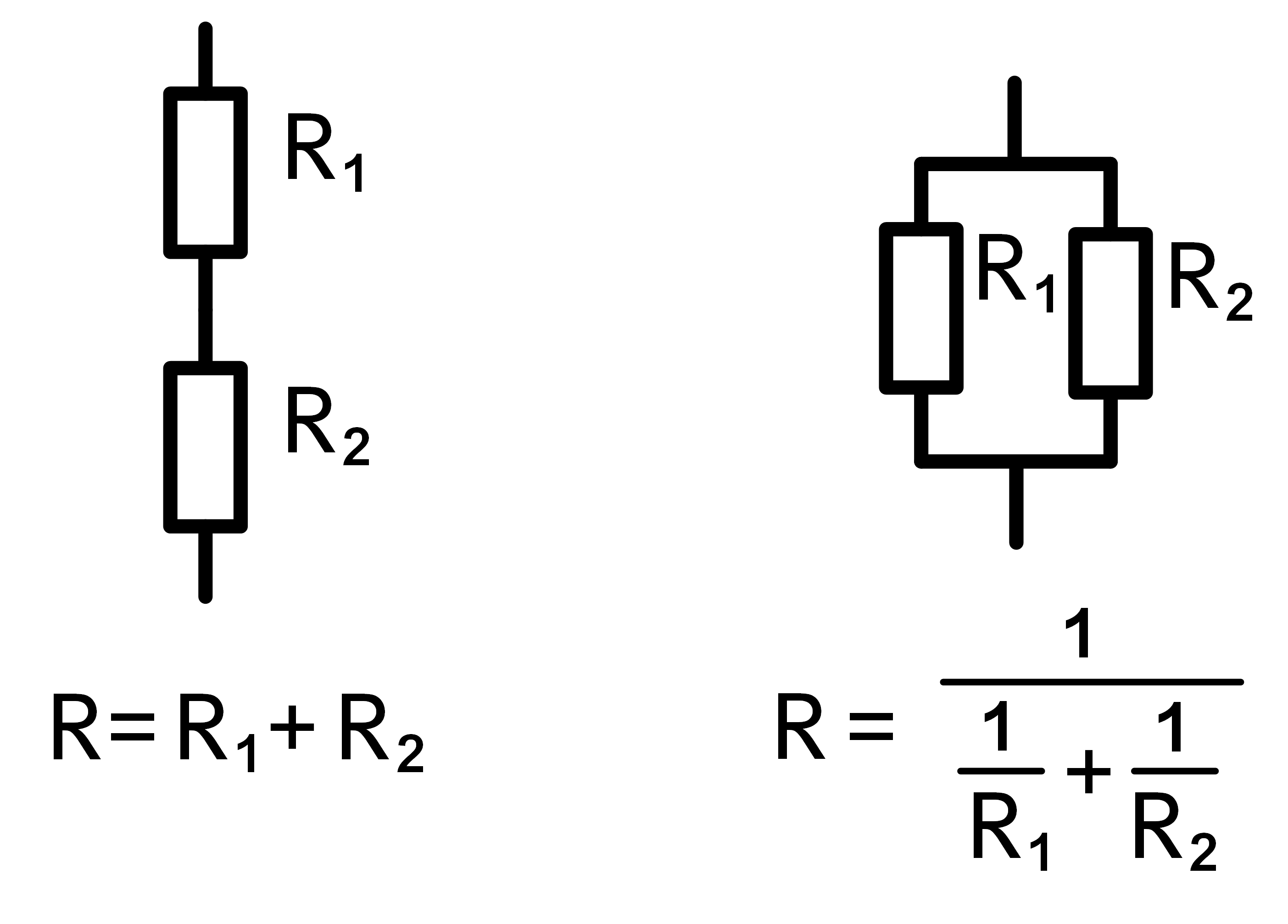
Picture 1: Two resistors combined in series and parallel

Picture 1: Two resistors combined in series and parallel
X
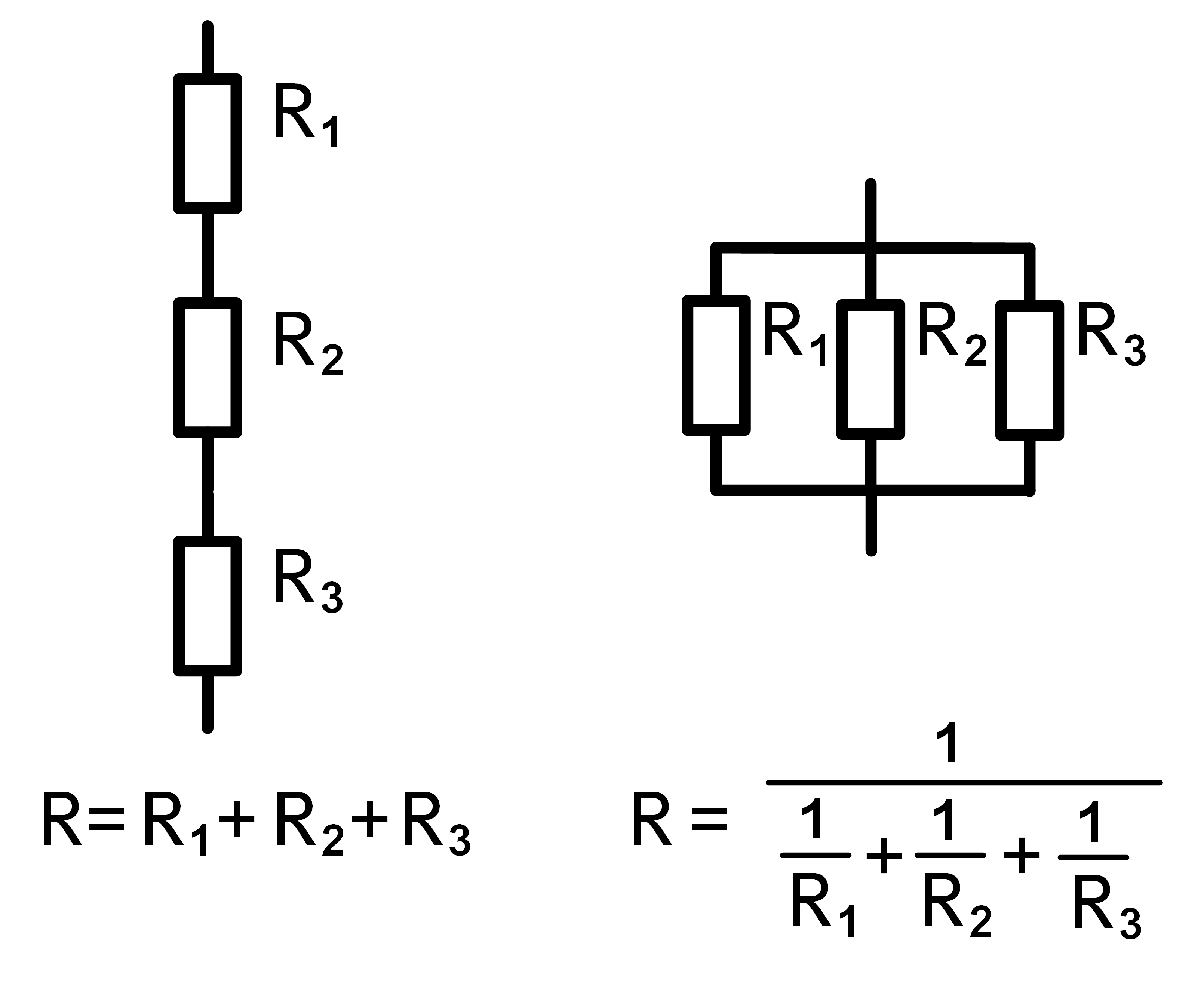
Picture 2: Three resistors combined in series and parallel

Picture 2: Three resistors combined in series and parallel
X
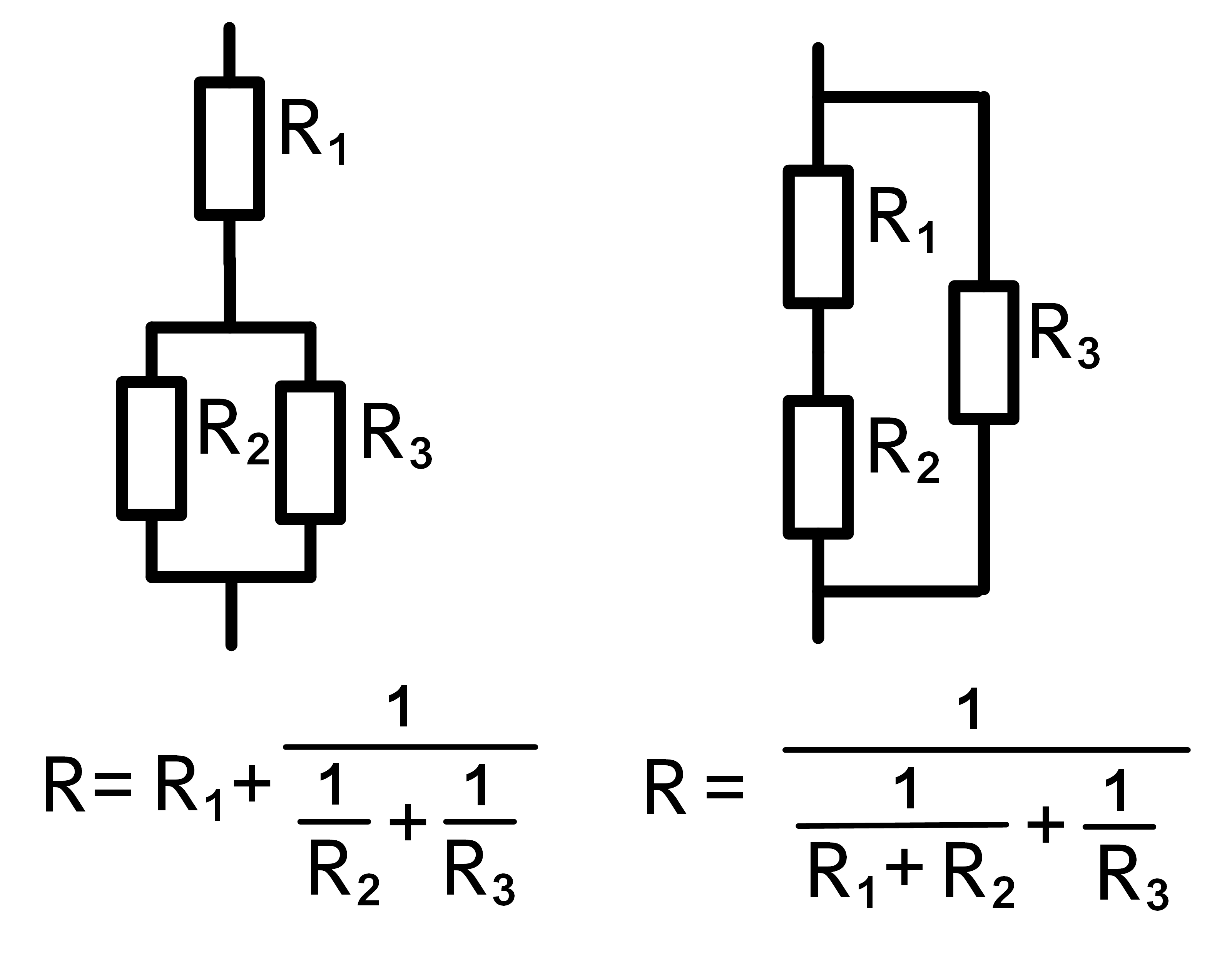
Picture 3: Mixed circuits with three resistors

Picture 3: Mixed circuits with three resistors